
LEPTON DEFINITION FULL
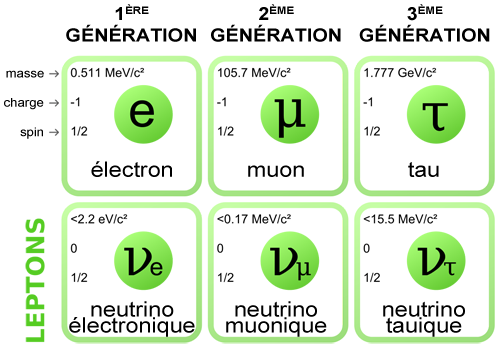
"Search for the lepton flavour violating decay μ + → e + γ with the full dataset of the MEG Experiment". "New limit on the lepton-flavor-violating decay mu+ to e+ gamma". "Evidence for oscillation of atmospheric neutrinos". "The Oscillating Neutrino: An introduction to neutrino masses and mixing" (PDF). ^ Slansky, Richard Raby, Stuart Goldman, Terry Garvey, Gerry (1997).Quarks & leptons, mesons, & baryons (PDF) (lecture notes). ^ Martin, Victoria J., Professor (25 February 2008). The definition of leptin is a peptide hormone that is produced by fat cells that plays a role in body weight regulation by acting on the hypothalamus to suppress appetite and burn fat stored in adipose tissue.ISBN 978-6-3 Tipler, Paul Llewellyn, Ralph (2002). Having non-zero mass means neutrinos also have individual speeds hence their oscillation rates will differ as well, and at the relativistic speeds neutrinos are inferred to travel at, each neutrino has its own, individual relativistic "clock", and hence whether the oscillation is mostly determined by distance travelled (like radio waves) or mostly determined by time measured on each neutrino's individual clock, in its rest frame or something in between, any way it goes, the neutrino flavour oscillations must be at least somewhat erratic.Ĭompounding injury with insult, above and beyond the consequences of neutrino oscillation, any direct or indirect interaction of the neutrinos with the Higgs field will change the neutrinos' chirality, further erasing what little evidence they carried indicating their original flavour or their future flavour-based identity. That alone scrambles the original lepton numbers: Effectively, all the balance maintained throughout the weak interaction itself is "trashed" as soon as the neutrinos move away from their place of creation, and since neutrinos have distinct masses they cannot have any one speed. Note the irony, that after all the meticulous bookkeeping of lepton numbers in every weak interaction, any neutrinos involved immediately begin to oscillate in flavour as they depart from the event. Mathematically, the lepton number L When this reversed-sign convention is observed, the baryon number is left unchanged, but the difference B − L is replaced with a sum: B + L, whose number value remains unchanged, since Lepton number is an additive quantum number, so its sum is preserved in interactions (as opposed to multiplicative quantum numbers such as parity, where the product is preserved instead). Is a conserved quantum number representing the difference between the number of leptons and the number of antileptons in an elementary particle reaction. The superparticle of a lepton is called a "slepton.In particle physics, lepton number (historically also called lepton charge) The charged leptons are all negative particles, their antiparticles are positively charged (for example, the antiparticle of the electron, e -, is a positron, e +). The other two charged leptons are the muon (µ) and the tau (τ), which are like electrons but much bigger. The best known charged lepton is the electron (e).

Of the six leptons, three have electric charge and three do not. The different varieties of the elementary particles are commonly called "flavors", and the neutrinos here are considered to have distinctly different flavor. There are six leptons: the electron, muon, and tau particles and their associated neutrinos. They are a family of particles that are different from the other known family of fermions, the quarks.Įlectrons are a well-known example that are found in ordinary matter. Leptons are said to be elementary particles that is, they do not appear to be made up of smaller units of matter. The six basic leptons: electrons, muons, tauons, electron neutrinos, mu neutrinos, and tau neutrinos, respectively Leptons are elementary particles with spin 1/2 (a fermion) that are not affected by strong nuclear force. lepton, any member of a class of subatomic particles that respond only to the electromagnetic force, weak force, and gravitational force and are not affected by the strong force.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
